Diflubenzuron
Le diflubenzuron est une substance active de produit phytosanitaire (ou produit phytopharmaceutique, ou pesticide), qui présente un effet insecticide, et qui appartient à la famille chimique des benzoylurées.
| Diflubenzuron | |
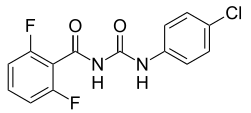
| |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| No CAS | |
| No ECHA | 100.047.740 |
| No CE | 252-529-3 |
| PubChem | |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C14H9ClF2N2O2 [Isomères] |
| Masse molaire[1] | 310,683 ± 0,015 g/mol C 54,12 %, H 2,92 %, Cl 11,41 %, F 12,23 %, N 9,02 %, O 10,3 %, |
| Propriétés physiques | |
| T° fusion | 239 °C |
| Solubilité | 0,08 mg L−1 dans l'eau à 25 °C |
| Pression de vapeur saturante | 9,00 × 10−10 mmHg à 25 °C |
| Précautions | |
| Directive 67/548/EEC | |
 N |
|
| Écotoxicologie | |
| DL50 | 4 640 mg kg−1 souris oral > 4 000 mg kg−1 souris s.c. 2 150 mg kg−1 souris i.p. |
| CL | > 35 g/m3/6 heures rat inhalation |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
En raison d'une certaine rémanence il semble pouvoir poser des problèmes écotoxiques dans les zones humides (où il est utilisé pour la démoustication) et en milieu marin[2] où via le lessivage ou une pollution aéroportée une partie des produits épandus arrivent.
Réglementation
Sur le plan de la réglementation des produits phytopharmaceutiques :
- pour l’Union européenne : cette substance active est inscrite à l’annexe I de la directive 91/414/CEE par la directive 2008/69/CE.
- pour la France : cette substance active est autorisée dans la composition de préparations bénéficiant d’une autorisation de mise sur le marché, mais n'en dispose pas, dans le cas présent d'un usage vétérinaire, sur les saumons d'élevage.
- en Norvège le diflubenzuron est autorisé comme pesticide pour éliminer le « Pou du saumon » dans l'élevage intensif du saumon, mais a provoqué une controverse écologique en 2011-2012. De nombreux articles ont été publiés à ce sujet[3].
Un reportage de France 3 avait révélé l'affaire au grand public en 2011. Il avait été précédé d'une demande officielle de la France à la Norvège, formulée le , par le Ministre de l'Agriculture, de l'Alimentation et de la Pêche de l'époque, Bruno Le Maire, à son homologue norvégienne[4], puis suivi par la réponse officielle, dans une lettre datée du , de la Ministre norvégienne de l'Alimentation, de l'Agriculture et des Pêches Lisbeth Berg-Hansen à son homologue français[5].
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- C. Alzieu (1977), “Toxicité et Persistance en Milieu Marin d’un Insecticide Dérivé des Benzoylurées: Le Diflubenzuron” Revue des Travaux de l’Institut des Pêches Maritimes, Vol. 41, No. 4, p. 317-324
- Les saumons d’élevage, gavés aux pesticides ?, sur le site bastamag.net, consulté le 7 août 2014
- [PDF]17 juin 2010 : lettre de la France à la Norvège, sur le site bastamag.net, consulté le 7 août 2014
- [PDF]23 juin 2010 : réponse de la Norvège à la France, sur le site bastamag.net, consulté le 7 août 2014
Voir aussi
Articles connexes
- Substance active d'un produit phytopharmaceutique
- Liste de substances actives de produits phytosanitaires
- Liste de substances actives de produits phytopharmaceutiques autorisées par l'Union Européenne
- Liste de substances actives de produits phytopharmaceutiques interdites par l'Union Européenne
- Éthoxyquine
- Poisson : élevage en eaux troubles (documentaire)
Bibliographie
- (en) N. Soltani, J. P. Delbecque and J. Delachambre, “Penetration and Insecticidal Activity of Diflubenzuron in Tenebrio molitor Pupae”, Pesticide Science, Vol. 14, No. 6, 1983, p. 615-622. doi:10.1002/ps.2780140609
- (en) N. Soltani and N. Soltani-Mazouni, “Diflubenzuron and Oogenesis in the Codling Moth, Cydia pomonella (L.)”, Pesticide Science, Vol. 34, No. 3, 1992, p. 257-261. doi:10.1002/ps.2780340311
- (en) N. Soltani, N. Pitoizet, N. Soltani-Mazouni and J. Delbecque, “Quantification par Chromatographie Liquide à Haute Perfermance du Diflubenzuron et du Flucyloxuron chez Tenebrio molitor et Thaumetopoea pytiocampa” ; Proceedings of International Symposium on Crop Protection, Vol. 59, No. 2, 1994, p. 481-486.
- (en) M. E. H. Khebbeb, J. Delachambre and N. Soltani, “Ingested Diflubenzuron Disturbed the Lipidic Metabolism during the Sexual Maturation of Mealworms”, Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, Vol. 58, No. 3, 1997, p. 209-217. doi:10.1006/pest.1997.2296
- (en) N. Soltani and S. M. Morsli, “Quantification du Dimilin par Chromatographie Liquide à Haute Performance: Étude de sa Dégradation dans L’eau de Mer” ; Journal de Recherche Océanographique, Vol. 28, 2003, p. 118-120.
- (en) D. J. MadderJ and W. L. Lockhart, “A Preliminary Study of the Effects of Diflubenzuron and Methoprene on Rainbow Trout (Salmo gairdneri Richardson)” ; Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, Vol. 20, No. 1, 1978, p. 66-70. doi:10.1007/BF01683487
- (en) E. G. Ellgaard, J. T. Barber, S. C. Tiwari and A. L. Friend, “An Analysis of the Swimming Behavior of Fish Exposed to the Insect Growth Regulators, Methoprene and Diflubenzuron” ; Mosquito News, Vol. 39, No. 2, 1979, p. 311-314.
- (en) M. T. Ahmed and A. H. Eid, “Accumulation of Diflubenzuron in Bolti Fish Orechromis niloticus” ; Nahrung, Vol. 35, No. 1, 1991, p. 27-31. doi:10.1002/food.19910350107
- (en) L. P. Maduenho and B. R. Martinez, “Acute Effects of Diflubenzuron on the Freshwater Fish Prochilodus lineatus” ; Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Vol. 148, 2008, p. 265-272.
- (en) C. H. Schaefer, E. F. Dupras, R. J. Stewart, L. W. Davidson and A. E. Colwell, “The Accumulation and Elimination of Diflubenzuron by Fish”; Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, Vol. 21, No. 1-2, 1979, p. 249-254.
- (en) K. M. S. Sundaram, S. B. Holmes, D. P. Kreutzweiser, A. Sundaram and P. D. Kingsbury (1991), “Environmental Persistence and Impact of Diflubenzuron in a Forest Aquatic Environment Following Aerial Application” ; Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, Vol. 20, No. 3, p. 313-324. doi:10.1007/BF01064396
- (en) A. Selvik, P. K. Hansen, A. Ervik and O. B. Samuelsen (2002), “The Stability and Persistence of Diflubenzuron in Marine Sediments Studied Under Laboratory Conditions and the Dispersion to the Sediment Under a Fish Farm Following Medication” ; Science of the Total Environment, Vol. 285, No. 1-3, p. 237-245.
- (en) L. S. Ricardo, J. M. C. Paulo and M. V. Eny (2009), “Analysis of Diflubenzuron in Tilapia Filet by HPLC-DAD” ; Journal of Chromatographic Science, Vol. 47, p. 785-788.
- (en) D. J. Austin and K. J. Hall, “A Method of Analysis for the Determination of Binapacryl, Bupirimate and Diflubenzuron on Apple Foliage and Fruit, and Its Application to Persistence Studies” ; Pesticide Science, Vol. 12, No. 5, 1981, p. 495-502. doi:10.1002/ps.2780120505
- (en) K. A. Barnes, J. R. Startin, S. A. Thorpe, S. L. Reynolds and R. J. Fussel, “Determination of the Pesticide Diflubenzuron Mushrooms by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionisation Mass Spectrometry” ; Journal of Chromatography A, Vol. 712, No. 1, 1995, p. 85-93. doi:10.1016/0021-9673(95)00481-2
- (en) E. Rodriguez, R. J. Barrio, A. Goicolea, R. Peche, Z. Gómez de Balugera and C. Sampedro (2001), “Presistance of the Insecticides Dimilin 45 ODC on Conifer Forest in an Atlantic Climate Ecosystem” ; Environmental Science Technology, Vol. 35, No. 18, p. 3804-3808. doi:10.1021/es0106927
- (en) S. A. Fischer and L. W. Hall (1992), “Environmental Concentrations and Aquatic Toxicity Data on Diflubenzuron (Dimilin)” ; Critical Reviews in Toxicology, Vol. 22, No. 1, p. 45-79. doi:10.3109/10408449209145321