Métacétamol
Le métacétamol est un composé organique. C'est un régioisomère non toxique du paracétamol, doté de propriétés analgésiques (anti-douleur) et antipyrétiques (anti-fièvre), mais qui n'a jamais été commercialisé[2].
| Métacétamol | |
| |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
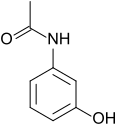
| Nom UICPA | N-(3-hydroxyphényl)acétamide |
| Synonymes |
3-hydroxyacétanilide, N-acétyl-méta-aminophénol, méta-acétyl-aminophénol |
| No CAS | |
| No ECHA | 100.009.717 |
| No CE | 210-687-0 |
| No RTECS | AE4100000 |
| PubChem | 12124 |
| ChEBI | 76987 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Apparence | poudre blanche cristallisée inodore |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C8H9NO2 [Isomères] |
| Masse molaire[1] | 151,162 6 ± 0,007 8 g/mol C 63,56 %, H 6 %, N 9,27 %, O 21,17 %, |
| Propriétés physiques | |
| T° fusion | 146 à 149 °C |
| T° ébullition | décomposition |
| Précautions | |
| SGH | |
 Attention |
|
| SIMDUT | |
Produit non contrôlé |
|
| Classification du CIRC | |
| Groupe 3 : Inclassable quant à sa cancérogénicité pour l'Homme | |
| Écotoxicologie | |
| DL50 | 1 025 mg kg−1 (souris, i.p.) |
| LogP | 0,73 |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
Une étude scientifique datant de 1980 a suggéré que le métacétamol pourrait être un analgésique et un antipyrétique plus sûr que le paracétamol[3].
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) « CHEBI:76987 - metacetamol », sur www.ebi.ac.uk.
- (en) Edward B. Nelson, « The pharmacology and toxicology of meta-substituted acetanilide I: acute toxicity of 3-hydroxyacetanilide in mice », Research communications in chemical pathology and pharmacology, .
Cet article est issu de wikipedia. Text licence: CC BY-SA 4.0, Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.