Oxyde de diphénylphosphine
L'oxyde de diphénylphosphine est un composé organophosphoré de formule chimique (C6H5)2P(O)H. Il se présente sous la forme d'un solide blanc à jaune-orangé soluble dans les solvants polaires organiques. Il est utilisé dans les réactions de Buchwald-Hartwig pour introduire un substituant diphénylphosphine (C6H5)2P–[3]. Comme l'acide phosphoreux H3PO3, l'oxyde de diphénylphosphine est en équilibre avec un tautomère mineur, l'hydroxydiphénylphosphine (C6H5)2POH[4].
| Oxyde de diphénylphosphine | |
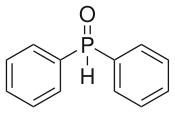
| |
| Structure de l'oxyde de diphénylphosphine | |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| No CAS | |
| PubChem | 6327869 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Apparence | solide inodore de couleur jaune-orangée[1] |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C12H11OP |
| Masse molaire[2] | 202,188 9 ± 0,010 7 g/mol C 71,28 %, H 5,48 %, O 7,91 %, P 15,32 %, |
| Précautions | |
| SGH[1] | |
 Attention |
|
| NFPA 704[1] | |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
L'oxyde de diphénylphosphine peut être obtenu en faisant réagir des esters phosphoniques, comme le diéthylphosphite (CH3CH2O)2P(O)H, avec des réactifs de Grignard. Il peut également être obtenu par l'hydrolyse partielle de la chlorodiphénylphosphine (C6H5)2PCl[3] ou de la diphénylphosphine (C6H5)2PH[5].
Les acides organophosphineux (en) sont réduits par l'hydrure de diisobutylaluminium (i-Bu2AlH)2 (DIBAL), où i-Bu représente le groupe isobutyle –CH2CH(CH3)2. Les phosphines secondaires obtenues sont des précurseurs de ligands phosphine[6].
Notes et références
- « Fiche du composé Diphenylphosphine oxide, 97% », sur Alfa Aesar (consulté le ).
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) Jeffrey O. Saunders, Zheng Wang et Kuiling Ding, « Diphenylphosphine Oxide », Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, (DOI 10.1002/047084289X.rd428.pub2, lire en ligne)
- (en) Mingchao Tan, Wenting Zheng, Lu Yang, Lihong Zhou et Qingle Zeng, « I2‐Catalyzed Oxidative N−P Cross‐Coupling of Diarylphosphine Oxides and Sulfoximines », Asian Journal of Organic Chemistry, vol. 8, no 11, , p. 2027-2031 (DOI 10.1002/ajoc.201900476, lire en ligne)
- (en) M. M. Rauhut et Helen A. Currier, « Oxidation of Secondary Phosphines to Secondary Phosphine Oxides », The Journal of Organic Chemistry, vol. 21, no 11, , p. 4626-4628 (DOI 10.1021/jo01069a102, lire en ligne)
- (en) Carl A. Busacca, Jon C. Lorenz, Paul Sabila, Nizar Haddad, Chris H. Senanayake, Scott E. Denmark et Christopher S. Regens, « Synthesis of Electron-Deficient Secondary Phosphine Ooxides and Secondary Phosphines: Bis[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]phosphine Oxide and Bis[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]phosphine », Organic Syntheses, vol. 84, , p. 242 (DOI 10.15227/orgsyn.084.0242, lire en ligne)
