Geoplanidae
Les Geoplanidae sont une famille de vers plats terrestres, de l'ordre des Tricladida.

Les Plathelminthes terrestres sont des animaux de corps allongé, plat, d'aspect lisse (ni pattes ni anneaux) et légèrement gluant. Ils n'ont ni yeux ni bouche visibles et se déplacent lentement[1].
Beaucoup de vers plats terrestres sécrètent de la tétrodotoxine — une toxine dangereuse — pour capturer leur proies. Il est donc déconseillé de les prendre à main nue.
Attitude à suivre
En cas de découverte d'un ver plat terrestre dans un jardin en France (pays où ils sont envahissants, nuisibles et sans prédateur connu), l'attitude à suivre est la suivante[2] - [1] :
- ne pas le toucher à main nue (on pourra le déplacer avec une allumette) ;
- le prendre en photo, avec une lumière suffisante et un repère d'étalonnage (par ex. une pièce de monnaie) pour évaluer sa longueur ;
- l’écraser (ou le placer dans un petit bocal étanche si on veut l'envoyer) ;
- adresser les photos (sous licence libre), voire le spécimen, à Jean-Lou Justine au Muséum national d'histoire naturelle en précisant bien vos coordonnées et le lieu et circonstances de collecte ; on peut aussi téléverser les photos avec l'application INPN espèces.
Phylogénie
- Arbre phylogénétique des Tricladida[3]
| Geoplanoidea |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Liste des genres

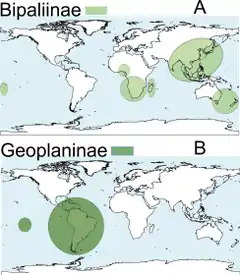
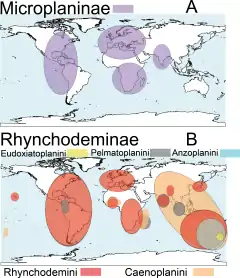
Selon World Register of Marine Species (18 mars 2015)[4], complété par NCBI (4 mars 2018)[5] :
- sous-famille Bipaliinae
- Bipalium Stimpson, 1857, dont l'espèce invasive Bipalium kewense
- Diversibipalium Kawakatsu, Ogren, Froehlich & Sasaki, 2002, dont l'espèce Diversibipalium multilineatum
- Humbertium Ogren & Sluys, 2001
- Novibipalium Kawakatsu, Ogren & Froehlich, 1998
- sous-famille Geoplaninae Stimpson, 1857
- Amaga Ogren & Kawakatsu, 1990
- Cephaloflexa Carbayo & Leal-Zanchet, 2003
- Choeradoplana Graff, 1896
- Cratera Carbayo, Alvarez-Presas, Olivares, Marques, Froehlich & Riutort, 2012
- Enterosyringa Ogren & Kawakatsu, 1990
- Geobia Diesing, 1862
- Geoplana Schultze & Müller, 1857
- Gigantea Ogren & Kawakatsu, 1990
- Gusana Froehlich, 1978
- Imbira Carbayo, Alvarez-Presas, Olivares, Marques, Froehlich & Riutort, 2012
- Issoca Froehlich, 1954
- Liana Froehlich, 1978
- Luteostriata Carbayo, 2010
- Matuxia Carbayo, Alvarez-Presas, Olivares, Marques, Froehlich & Riutort, 2012
- Notogynaphallia Ogren & Kawakatsu, 1990
- Obama Carbayo, Alvarez-Presas, Olivares, Marques, Froehlich & Riutort, 2012
- Paraba Carbayo, Alvarez-Presas, Olivares, Marques, Froehlich & Riutort, 2012
- Pasipha Ogren & Kawakatsu, 1990
- Polycladus Blanchard, 1845
- Pseudogeoplana Ogren & Kawakatsu, 1990
- Supramontana Carbayo & Leal-Zanchet, 2003
- Xerapoa Froehlich, 1955
- sous-famille Microplaninae Pantin, 1953
- Amblyplana Graff, 1896
- Diporodemus Hyman, 1938
- Geobenazzia Minelli, 1974
- Incapora Du Bois-Reymond Marcus, 1953
- Microplana Vejdovsky, 1890
- Othelosoma Gray, 1869
- Pseudartiocotylus Ikeda, 1911
- Statomicroplana Kawakatsu, Froehlich, Jones, Ogren & Sasaki, 2003
- sous-famille Rhynchodeminae Graff, 1896
- tribu Anzoplanini Winsor 2006
- Anzoplana Winsor, 2006
- Marionfyfea Winsor, 2011 dont l'espèce invasive en Europe Marionfyfea adventor
- tribu Argaplanini Winsor 2011
- Argaplana Winsor, 2011
- tribu Caenoplanini Ogren & Kawakatsu, 1991
- Arthurdendyus Jones, 1999, dont l'espèce invasive en Europe Arthurdendyus triangulatus
- Artioposthia von Graff, 1896
- Australopacifica Ogren & Kawakatsu, 1991
- Australoplana Winsor, 1991
- Caenoplana Moseley, 1877
- Coleocephalus Fyfe, 1953
- Endeavouria Ogren & Kawakatsu, 1991
- Fletchamia Winsor, 1991
- Kontikia C. G. Froehlich, 1955
- Lenkunya Winsor, 1991
- Newzealandia Ogren & Kawakatsu, 1991
- Pimea Winsor, 1991
- Reomkago Winsor, 1991
- Tasmanoplana Winsor, 1991
- Timyma E. M. Froehlich, 1978
- tribu Eudoxiatopoplanini Winsor 2009
- Eudoxiatopoplana Winsor, 2009
- tribu Pelmatoplanini Ogren & Kawakatsu, 1991
- Beauchampius Ogren & Kawakatsu, 1991
- Pelmatoplana Graff, 1896
- tribu Rhynchodemini Heinzel, 1929
- Anisorhynchodemus Kawakatsu, Froehlich, Jones, Ogren & Sasaki, 2003
- Cotyloplana Spencer, 1892
- Digonopyla Fischer, 1926
- Dolichoplana Moseley, 1877
- Platydemus Graff, 1896
- Rhynchodemus Leidy, 1851
- tribu Anzoplanini Winsor 2006

_(5780287991).jpg.webp)

 Cephaloflexa araucariana
Cephaloflexa araucariana Choeradoplana iheringi
Choeradoplana iheringi
 Geoplana burmeisteri
Geoplana burmeisteri
 Luteostriata graffi
Luteostriata graffi_-_Saveuse%252C_France.jpg.webp)
 Obama ladislavii
Obama ladislavii Paraba multicolor
Paraba multicolor
 Polycladus gayi
Polycladus gayi Pseudogeoplana reticulata
Pseudogeoplana reticulata Rhynchodemus sylvaticus
Rhynchodemus sylvaticus Supramontana irritata
Supramontana irritata
Références taxinomiques
- (en) Référence World Register of Marine Species : taxon Geoplanidae Stimpson, 1857 (+ liste genres + liste espèces)
- (fr+en) Référence ITIS : Geoplanidae
- (en) Référence Animal Diversity Web : Geoplanidae
- (en) Référence uBio : site déclaré ici indisponible le 7 avril 2023
- (en) Référence Catalogue of Life : Geoplanidae Stimpson, 1857 (consulté le )
- (en) Référence Fauna Europaea : Geoplanidae Stimpson, 1857 (consulté le )
- (en) Référence NCBI : Geoplanidae (taxons inclus)
Liens externes
- Page d'appel à témoins de l'Inventaire National du Patrimoine Naturel sur des Geoplanidae invasifs en France.
Bibliographie
- Stimpson, 1857 : Prodromus descriptionis animalium evertebratorum, quae in Expeditione ad Oceanum Pacificum Septentrionalem a Republica Federata missa, Johanne Rodgers Duce, observavit et descripsit. Pars I, Turbellaria Dendrocoela. Proceedings of Ihe Academy of natural sciences of Philadelphia 9 p. 19-31.
- Tyler, Schilling, Hooge & Bush 2006 : Turbellarian taxonomic database. Version 1.5 Base de données
Notes et références
- « Que faire si je trouve un Plathelminthe? » sur le site personnel de Jean-Lou Justine, spécialiste français des Plathelminthes au Muséum national d'histoire naturelle de Paris.
- https://jardinage.lemonde.fr/dossier-3134-plathelminthes.html
- R. Sluys, M. Kawakatsu, M. Riutort et J. Baguñà, « A new higher classification of planarian flatworms (Platyhelminthes, Tricladida) », Journal of Natural History, vol. 43, nos 29–30, , p. 1763–1777 (DOI 10.1080/00222930902741669)
- World Register of Marine Species, consulté le 18 mars 2015
- NCBI, consulté le 4 mars 2018