Acide gamma-amino-bêta-hydroxybutyrique
L'acide γ-amino-β-hydroxybutyrique (GABOB) est un métabolite endogène analogue au GABA, neurotransmetteur important du cerveau, et susceptible de ce fait de jouer lui-même le rôle de neurotransmetteur[2] - [3]. Il possède un effet inhibiteur plus puissant que le GABA sur le système nerveux central, peut-être en relation avec sa meilleure capacité à franchir la barrière hémato-encéphalique[3] - [4].
| Acide γ-amino-β-hydroxybutyrique | |
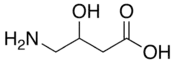  Structure de l'acide γ-amino-β-hydroxybutyrique |
|
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | acide 4-amino-3-hydroxybutanoïque |
| Synonymes |
3-hydroxy-GABA |
| No CAS | |
| No ECHA | 100.011.916 |
| PubChem | 2149 |
| ChEBI | 16080 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C4H9NO3 [Isomères] |
| Masse molaire[1] | 119,119 2 ± 0,004 9 g/mol C 40,33 %, H 7,62 %, N 11,76 %, O 40,29 %, |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
Il possède également un effet antiépileptique qui le fait utiliser comme médicament dans cette indication ; cet effet antiépileptique est cependant assez faible lorsqu'il est utilisé seul, ce qui fait qu'on l'emploie comme traitement complémentaire parallèlement à un autre antiépileptique[5] - [6].
Le GABOB possède deux énantiomères, l'isomère (3S) D-GABOB étant deux fois plus puissant que l'isomère (3R) L-GABOB[7].
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) Gian B. Melis, A. M. Paoletti, V. Mais, N. M. Mastrapasqua, F. Strigini, F. Fruzzetti, G. Guarnieri, M. Gambacciani et P. Fioretti, « Dose-related effects of γ-amino β-hydroxy butyric acid (GABOB) infusion on growth hormone secretion in normal women », Journal of Endocrinological Investigation, vol. 5, no 2, , p. 101-106 (DOI 10.1007/BF03350499, lire en ligne)
- (en) Hayashi Takashi, « The inhibitory action of β-hydroxy-γ-aminobutyric acid upon the seizure following stimulation of the motor cortex of the dog », The Journal of Physiology, vol. 145, no 3, , p. 570-578 (DOI 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006163, lire en ligne)
- (en) D. De Maio et G. Pasquariello, « Gamma-amino-beta-hydroxybutyric acid (GABOB) and brain serotonin », Psychopharmacologia, vol. 5, no 1, , p. 84-86 (PMID 14085623, DOI 10.1007/BF00405577, lire en ligne)
- (it) R. Chemello, D. Giaretta, A. Pellegrini et G. Testa, « Effect of gamma-amino-beta-hydroxybutyric acid (GABHB) on experimentally-induced epileptic activity », Rivista di Neurologia, vol. 50, no 4, , p. 253-268 (PMID 7466221)
- (en) E. García-Flores et R. Farías, « γ-Amino-β-Hydroxybutyric Acid as Add-On Therapy in Adult Patients with Severe Focal Epilepsy », Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery, vol. 69, nos 1-4, , p. 243-246 (PMID 9711762, DOI 10.1159/000099882, lire en ligne)
- (en) E. Roberts, D. N. Krause, E. Wong et A. Mori, « Different efficacies of D- and L-gamma-amino-beta-hydroxybutyric acids in GABA receptor and transport test systems », Journal of Neurosciences, vol. 1, no 2, , p. 132-140 (PMID 6267220, lire en ligne)