Platyzoa
Les Platyzoaires (Platyzoa, du grec platús 'plat' et zōon 'animal') forment un super-embranchement d'animaux protostomiens, ils réunissent les vers plats et les animaux qui leur sont phylogénétiquement proches.
Histoire du taxon
Le taxon a été créé par Thomas Cavalier-Smith en 1998[1]. Il comprend tous les gnathifères en son sein.
Peterson & Eernisse 2001[2] y ont remplacé les Gastrotriches par les Cycliophores.
Liste des sous-taxons
- embranchement Acanthocephala Rudolphi, 1802
- embranchement Gastrotricha Metschnikoff, 1865
- embranchement Gnathostomulida Sterrer, 1972
- embranchement Micrognathozoa Kristensen & Funch, 2000
- embranchement Orthonectida Giard, 1877
- embranchement Platyhelminthes Minot, 1876
- embranchement Rhombozoa van Beneden, 1876
- embranchement Rotifera Cuvier, 1817
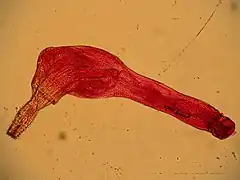 Corynosoma wegeneri (Acanthocephala)
Corynosoma wegeneri (Acanthocephala)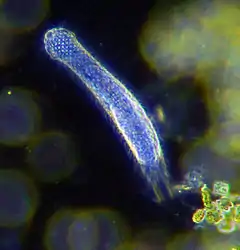 un Gastrotricha
un Gastrotricha
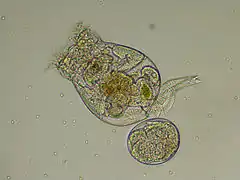
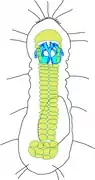 Schéma de Limnognathia maerski, l'unique Micrognathozoa connu
Schéma de Limnognathia maerski, l'unique Micrognathozoa connu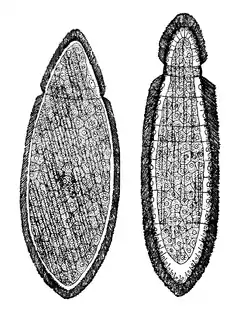 Schéma d'un Orthonectida
Schéma d'un Orthonectida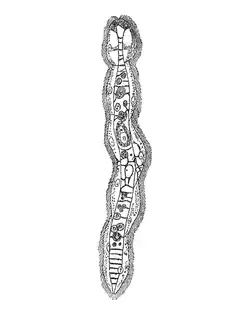 Schéma de Dicyema macrocephalum (Rhombozoa)
Schéma de Dicyema macrocephalum (Rhombozoa)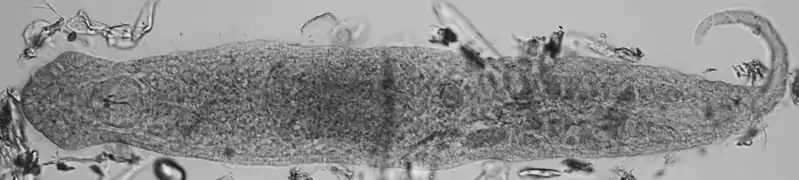 Gnathostomula paradoxa (Gnathostomulida)
Gnathostomula paradoxa (Gnathostomulida)
Références taxinomiques
- (fr+en) Référence ITIS : Platyzoa
- (en) Référence Tree of Life Web Project : Platyzoa
- (en) Référence Animal Diversity Web : Platyzoa
- (fr) Référence Catalogue of Life : Platyzoa
Notes et références
- Thomas Cavalier-Smith, 1998. A revised six-kingdom system of life. Biol. Rev. 73: 203-266.
- Kevin J. Peterson & Douglas J. Eernisse, 2001. Animal phylogeny and the ancestry of Bilaterian.
- Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS), www.itis.gov, CC0 https://doi.org/10.5066/F7KH0KBK, consulté le 7 mars 2016
Cet article est issu de wikipedia. Text licence: CC BY-SA 4.0, Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.
