Khoratpithecus
Khoratpithèque
Khoratpithecus
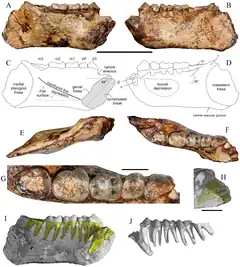
Khoratpithecus (Khoratpithèque en français) est un genre éteint de singes de la sous-famille des ponginés. Il vivait en Asie du Sud-Est durant le Miocène moyen et supérieur, il y a entre 12,2 et 7 millions d'années.
Arbre phylogénétique
Khoratpithecus fait partie de la sous-famille des ponginés, que l'on trouvait au Miocène dans toute l'Asie méridionale, de la Turquie jusqu'à la Chine. D'après sa morphologie, il est, parmi les différents ponginés fossiles, le genre le plus proche de l'Orang-outan actuel.
Phylogénie des genres de ponginés, d'après James Birx et al. (2010)[1] et David Begun (2015)[2] :
| Ponginae |
| ||||||||||||||||||
Liste d'espèces
Le genre Khoratpithecus comprend trois espèces, qui vivaient au Miocène en Asie du Sud-Est :
Notes et références
- (en) H. James Birx (dir.), 21st Century Anthropology : A Reference Handbook, partie IX, chapitre 55, p. 553-554, vol. 2, Sage Publications, (lire en ligne)
- (en) David R. Begun, The real Planet of the Apes : A new Story of human Origins, Princeton University Press, (lire en ligne)
- (en) Chaimanee et al., Khoratpithecus piriyai, A Late Miocene Hominoid of Thailand, American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2006, lire en ligne
- (en) Jean-Jacques Jaeger et al., « First Hominoid from the Late Miocene of the Irrawaddy Formation (Myanmar) », PLoS ONE, vol. 6, no 4, , p. 1–14 (PMID 21533131, PMCID 3080362, DOI 10.1371/journal.pone.0017065)
Bibliographie
- (en) David R. Begun, « The Miocene hominoid Radiations », A Companion to Paleoanthropology, Oxford, Wiley-Blackwell, , p. 398-415 (lire en ligne)
- (en) David R. Begun, The real Planet of the Apes : A new Story of human Origins, Princeton University Press, (lire en ligne)
Voir aussi
Article connexe
Liens externes
- Ressources relatives au vivant :
Cet article est issu de wikipedia. Text licence: CC BY-SA 4.0, Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.