Vicianine
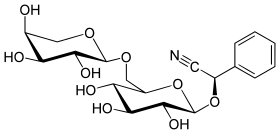
La vicianine est un composé aromatique de la famille des glycosides cyanogènes. Elle est constituée du vicianose, un disaccharide, et du (R)-mandélonitrile pour la partie aglycone.
| Vicianine | |
| |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Nom systématique | (2R)-2-phényl-2-[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[[(2S,3R,4S,5S)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxyméthyl]oxan-2-yl]oxyacétonitrile |
| Synonymes |
mandélonitrile bêta-vicianoside |
| No CAS | |
| PubChem | 656493 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C19H25NO10 |
| Masse molaire[1] | 427,402 5 ± 0,020 2 g/mol C 53,39 %, H 5,9 %, N 3,28 %, O 37,43 %, |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
L'enzyme vicianine bêta-glucosidase catalyse l'hydrolyse de la (R)-vicianine en mandélonitrile et vicianose. On trouve le composé et l'enzyme dans les graines de Vicia angustifolia[2].
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- Y. O. Ahn, H. Saino, M. Mizutani, B.-i. Shimizu et K. Sakata, « Vicianin hydrolase is a novel cyanogenic beta-glycosidase specific to beta-vicianoside (6-O-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside) in seeds of Vicia angustifolia », Plant and Cell Physiology, vol. 48, no 7, , p. 938 (PMID 17548373, DOI 10.1093/pcp/pcm065)
Cet article est issu de wikipedia. Text licence: CC BY-SA 4.0, Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.