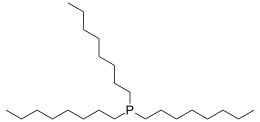
Trioctylphosphine
La trioctylphosphine, ou TOP, est un composé organophosphoré de formule chimique P(C8H17)3. C'est un réactif couramment utilisé pour la synthèse de nanoparticules. La trioctylphosphine réagit avec l'oxygène pour former de l'oxyde de trioctylphosphine.
| Trioctylphosphine | |||
| |||
| Structure de la trioctylphosphine | |||
| Identification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | trioctylphosphane | ||
| Synonymes |
TOP |
||
| No CAS | |||
| No ECHA | 100.022.940 | ||
| No CE | 225-234-2 | ||
| No RTECS | SZ3450000 | ||
| PubChem | 20851 | ||
| SMILES | |||
| InChI | |||
| Propriétés chimiques | |||
| Formule | C24H51P |
||
| Masse molaire[1] | 370,635 5 ± 0,022 8 g/mol C 77,77 %, H 13,87 %, P 8,36 %, |
||
| Précautions | |||
| SGH[2] | |||
 Danger |
|||
| Transport[2] | |||
|
|||
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |||
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- Fiche Sigma-Aldrich du composé Trioctylphosphine 97%, consultée le 14 avril 2018.
Cet article est issu de wikipedia. Text licence: CC BY-SA 4.0, Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.