Stigmastane
Le Stigmastane, aussi connu sous l'appellation 24R-éthylcholestane, est un triterpène tétracyclique. Avec le cholestane et l'ergostane, ce stérane est utilisé comme biomarqueur des eucaryotes précoces[3].
| Stigmastane [1] | |
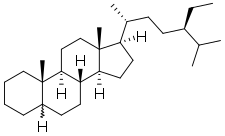 Structure du stigmastane |
|
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | (1R,3aS,3bR,5aΞ,9aS,9bS,11aR)-1-[(2R,5R)-5-Ethyl-6-methylheptan-2-yl]-9a,11a-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene |
| No CAS | |
| PubChem | |
| ChEBI | 26773 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C29H52 |
| Masse molaire[2] | 400,723 2 ± 0,026 8 g/mol C 86,92 %, H 13,08 %, |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
Son nom est dérivé du stigmastérol, un phytostérol végétal.
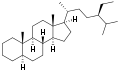 5α-Stigmastane
5α-Stigmastane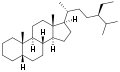 5β-Stigmastane
5β-Stigmastane
Références
- International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013, The Royal Society of Chemistry, , 1531 p. (ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4, DOI 10.1039/9781849733069)
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- Jochen J. Brocks, Amber J. M. Jarrett, Eva Sirantoine, Christian Hallmann, Yosuke Hoshino et Tharika Liyanage, « The rise of algae in Cryogenian oceans and the emergence of animals », Nature, vol. 548, no 7669, , p. 578–581 (PMID 28813409, DOI 10.1038/nature23457, Bibcode 2017Natur.548..578B, S2CID 205258987)
Cet article est issu de wikipedia. Text licence: CC BY-SA 4.0, Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.