Phéophytine a
La phéophytine a est un tétrapyrrole de la famille des chlorines correspondant à une molécule de chlorophylle a dépourvue de son cation central de magnésium Mg2+. Comme les autres phéophytines, elle intervient dans la photosynthèse comme premier transporteur d'électrons intermédiaire dans la chaîne respiratoire du photosystème II chez les plantes (PS II), et du centre réactionnel photosynthétique des bactéries pourpres (RC P870)[2].
| Phéophytine a | |
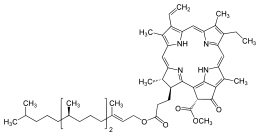 Structure de la phétophytine a |
|
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | méthyl(3S,4S,21R)-14-éthyl-4,8,13,18-tétraméthyl-20-oxo-3-(3-oxo-3-{[(2E,7R,11R)-3,7,11,15-tétraméthylhexadéc-2-én-1-yl]oxy}propyl)-9-vinylphorbine-21-carboxylate |
| No CAS | |
| No ECHA | 100.009.120 |
| No CE | 210-031-3 |
| PubChem | 5459387 |
| ChEBI | 44898 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C55H74N4O5 [Isomères] |
| Masse molaire[1] | 871,199 9 ± 0,051 5 g/mol C 75,83 %, H 8,56 %, N 6,43 %, O 9,18 %, |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) Vyacheslav V. Klimov, « Discovery of pheophytin function in the photosynthetic energy conversion as the primary electron acceptor of Photosystem II », Photosynthesis Research, vol. 76, nos 1-3, , p. 247-253 (lire en ligne) DOI 10.1023/A:1024990408747
Cet article est issu de wikipedia. Text licence: CC BY-SA 4.0, Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.