Dioxyde de tellure
Le dioxyde de tellure (TeO2) est un oxyde de tellure. Il se rencontre sous trois formes différentes :
- le tétragone synthétique et incolore qu'est la paratellurite, α-TeO2[3]. La plupart des informations concernant les réactions chimiques ont été obtenues par des études relatives à la paratellurite[4] ;
- la tellurite β-TeO2, un minéral jaunâtre ;
- γ-TeO2, métastable, de structure orthorhombique : groupe d'espace P212121 (no 18) avec a = 489,8 pm, b = 857,6 pm, c = 435,1 pm et Z (nombre d'unités par maille) = 4[5].
| Dioxyde de tellure | |
 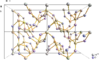 |
|
| Poudre de tellure et structure de α-TeO2. | |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| No CAS | |
| No ECHA | 100.028.357 |
| No CE | 231-193-1 |
| PubChem | 62638 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Apparence | solide blanc |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | TeO2 |
| Masse molaire[1] | 159,6 ± 0,03 g/mol O 20,05 %, Te 79,95 %, |
| Propriétés physiques | |
| T° fusion | 732 °C |
| T° ébullition | 1 245 °C |
| Solubilité | négligeable (solvant : acide, alcali) |
| Précautions | |
| SGH[2] | |
    |
|
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
Notes et références
- (en) Cet article est partiellement ou en totalité issu de l’article de Wikipédia en anglais intitulé « Tellurium dioxide » (voir la liste des auteurs).
- Yanlu Li, Weiliu Fan, Honggang Sun, Xiufeng Cheng, Pan Li, Xian Zhao, Structural, electronic, and optical properties of α, β, and γ-TeO2, Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, vol. 107, 093506. DOI 10.1063/1.3406135.
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- PubChem CID 62638
- Greenwood et Earnshaw 1984, p. 911
- McWhinnie 1995
- J.C. Champarnaud-Mesjard, S. Blanchandin, P. Thomas, A. Mirgorodsky,T. Merle-Méjean, B. Frit, Crystal structure, Raman spectrum and lattice dynamics of a new metastable form of tellurium dioxide: γ-TeO2, Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2000, vol. 61, pp. 1499–1507.
Bibliographie
- W. R. McWhinnie, « Tellurium - Inorganic chemistry », dans Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry, R. Bruce King, John Wiley & Sons, (ISBN 978-0-471-93620-6)
- (en) Norman N. Greenwood et Alan Earnshaw, Chemistry of the Elements, Oxford, Pergamon Press, (ISBN 0-08-022057-6)
Cet article est issu de wikipedia. Text licence: CC BY-SA 4.0, Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.