Cycle du fer
Le cycle du fer (Fe) est le cycle biogéochimique du fer à travers l'atmosphère, l'hydrosphère, la biosphère et la lithosphère. Alors que le fer est très abondant dans la croûte terrestre[10], il est moins courant dans les eaux de surface oxygénées. Le fer est un micronutriment essentiel à la productivité primaire[11] et un nutriment limitant dans l'océan Austral, le Pacifique équatorial oriental et le Pacifique subarctique. Ces régions océaniques sont dites à haute teneur en nutriments et à faible teneur en chlorophylle (HNLC)[12].
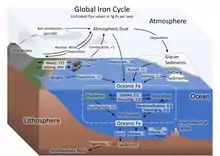
Le fer existe sous plusieurs forme de degré d'oxydation allant de -2 à +7 ; cependant, il est principalement présent sous forme +2 ou +3 sur Terre et est un métal redox primaire actif[13]. Le cycle du fer entre ses degrés d'oxydation +2 et +3 est appelé cycle du fer. Ce processus peut être entièrement abiotique ou facilité par des microorganismes, notamment des bactéries oxydant le fer. Les processus abiotiques comprennent la rouille des métaux ferreux, où Fe2+ est oxydé abiotiquement en Fe3+ en présence d'oxygène, et la réduction de Fe3+ en Fe2+ par des minéraux sulfurés de fer. Le cycle biologique du Fe2+ se fait par oxydation du fer et réduction des microbes[14] - [15].
Références
- (en) « A dynamic marine iron cycle module coupled to the University of Victoria Earth System Model: the Kiel Marine Biogeochemical Model 2 for UVic 2.9 », Geoscientific Model Development, vol. 8, no 5, , p. 1357–1381 (DOI 10.5194/gmd-8-1357-2015, Bibcode 2015GMD.....8.1357N)
- (en) « Global iron connections between desert dust, ocean biogeochemistry, and climate », Science, vol. 308, no 5718, , p. 67–71 (PMID 15802595, DOI 10.1126/science.1105959, Bibcode 2005Sci...308...67J)
- (en) « The iron biogeochemical cycle past and present », Geochemical Perspectives, vol. 1, , p. 1–232 (DOI 10.7185/geochempersp.1.1, lire en ligne)
- (en) « Forging the Anthropogenic Iron Cycle », Environmental Science & Technology, vol. 41, no 14, , p. 5120–5129 (PMID 17711233, DOI 10.1021/es062761t, Bibcode 2007EnST...41.5120W)
- « Modeling organic iron-binding ligands in a three-dimensional biogeochemical ocean model. », Marine Chemistry, vol. 173, , p. 67–77 (DOI 10.1016/j.marchem.2014.11.008, lire en ligne)
- (en) « Anthropogenic combustion iron as a complex climate forcer », Nature Communications, vol. 9, no 1, , p. 1593 (PMID 29686300, PMCID 5913250, DOI 10.1038/s41467-018-03997-0, Bibcode 2018NatCo...9.1593M)
- (en) « The Irony of Iron - Biogenic Iron Oxides as an Iron Source to the Ocean », Frontiers in Microbiology, vol. 6, , p. 1502 (PMID 26779157, PMCID 4701967, DOI 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01502)
- (en) « Surface ocean iron fertilization: The role of airborne volcanic ash from subduction zone and hot spot volcanoes and related iron fluxes into the Pacific Ocean », Global Biogeochemical Cycles, vol. 25, no 4, , n/a (DOI 10.1029/2009GB003761, Bibcode 2011GBioC..25.4001O, lire en ligne)
- (en) « Seasonal distributions of aeolian iron fluxes to the global ocean », Geophysical Research Letters, vol. 28, no 1, , p. 29–32 (DOI 10.1029/2000GL011926, Bibcode 2001GeoRL..28...29G)
- (en) « Abundance of chemical elements in the continental crust: a new table », Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, vol. 28, no 8, , p. 1273–1285 (DOI 10.1016/0016-7037(64)90129-2, Bibcode 1964GeCoA..28.1273T)
- (en) « The integral role of iron in ocean biogeochemistry », Nature, vol. 543, no 7643, , p. 51–59 (PMID 28252066, DOI 10.1038/nature21058, Bibcode 2017Natur.543...51T, lire en ligne)
- (en) « Iron deficiency limits phytoplankton growth in the north-east Pacific subarctic », Nature, vol. 331, no 6154, , p. 341–343 (DOI 10.1038/331341a0, Bibcode 1988Natur.331..341M)
- (en) « The interplay of microbially mediated and abiotic reactions in the biogeochemical Fe cycle », Nature Reviews. Microbiology, vol. 12, no 12, , p. 797–808 (PMID 25329406, DOI 10.1038/nrmicro3347)
- (en) « Ecosystem functioning from a geomicrobiological perspective – a conceptual framework for biogeochemical iron cycling », Environmental Chemistry, vol. 7, no 5, , p. 399 (DOI 10.1071/EN10040)
- Kappler, Andreas; Straub, Kristina L. (2005-01-01). "Geomicrobiological Cycling of Iron". Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry. 59 (1): 85–108. doi:10.2138/rmg.2005.59.5. ISSN 1529-6466.