Bialaphos
Le bialaphos est un tripeptide correspondant à la L-alanyl-L-alanyl-phosphinotricine. Il a été isolé à partir de deux bactéries du genre Streptomyces vivant dans le sol, Streptomyces hygroscopicus[2] et Streptomyces viridochromogenes. Il possède des propriétés herbicides dues à la phosphinotricine, qui est le composé biologiquement actif.
| Bialaphos | |
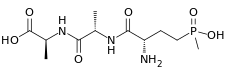 Structure du bialaphos |
|
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | acide (2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-amino-4-[hydroxy(méthyl)phosphoryl]butanoyl]
amino]propanoyl]amino]propanoïque |
| Synonymes |
bilanafos, |
| No CAS | |
| No ECHA | 100.113.731 |
| PubChem | 5462314 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C11H22N3O6P |
| Masse molaire[1] | 323,282 6 ± 0,012 7 g/mol C 40,87 %, H 6,86 %, N 13 %, O 29,69 %, P 9,58 %, |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) Takeshi Murakami, Hiroyuki Anzai, Satoshi Imai, Atsuyuki Satoh, Kozo Nagaoka et Charles J. Thompson, « The bialaphos biosynthetic genes of Streptomyces hygroscopicus: Molecular cloning and characterization of the gene cluster », Molecular and General Genetics MGG, vol. 205, no 1, , p. 42-53 (lire en ligne) DOI 10.1007/BF02428031
Cet article est issu de wikipedia. Text licence: CC BY-SA 4.0, Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.