Queuosine
La queuosine est un nucléoside rare présent dans certains ARN de transfert chez les bactéries et les eucaryotes[2] - [3]. Elle a été écouverte chez E. coli, où elle occupe la première position des anticodons d'ARNt pour l'histidine, l'acide aspartique, l'asparagine et l'histidine, et s'est révélée par la suite être très largement distribuée[4]. La première position d'un anticodon d'ARNt s'apparie à la troisième position d'un codon d'ARN messager par wobble pairing, où la queuosine améliore la fidélité de la traduction génétique[5] - [6] - [7].
| Queuosine | |
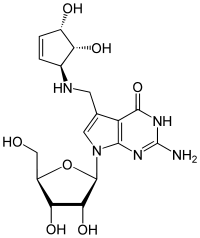 Structure de la queuosine |
|
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | 2-amino-5-({[(1S,4S,5R)-4,5-dihydroxycyclopent-2-én-1-yl]amino}méthyl)-7-(β-D-ribofuranosyl)-1,7-dihydro-4H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-one |
| Synonymes |
Nucléoside Q |
| No CAS | |
| PubChem | 42119 |
| ChEBI | 60193 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C17H23N5O7 |
| Masse molaire[1] | 409,393 8 ± 0,018 3 g/mol C 49,87 %, H 5,66 %, N 17,11 %, O 27,36 %, |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) Dirk Iwata-Reuyl, « Biosynthesis of the 7-deazaguanosine hypermodified nucleosides of transfer RNA », Bioorganic Chemistry, vol. 31, no 1, , p. 24-43 (lire en ligne) DOI 10.1016/S0045-2068(02)00513-8
- (en) Rana C. Morris et Mark S. Elliott, « Queuosine Modification of tRNA: A Case for Convergent Evolution », Molecular Genetics and Metabolism, vol. 74, nos 1-2, , p. 147-159 (lire en ligne) DOI 10.1006/mgme.2001.3216
- (en) Fumio Harada et Susumu Nishimura, « Possible anticodon sequences of tRNAHis, tRNAAsn, and tRNAAsp from Escherichia coli. Universal presence of nucleoside O in the first position of the anticodons of these transfer ribonucleic acid », Biochemistry, vol. 11, no 2, , p. 301-308 (lire en ligne) DOI 10.1021/bi00752a024
- (en) Mariann Bienz et Eric Kubli, « Wild-type tRNATyrG reads the TMV RNA stop codon, but Q base-modified tRNATyrQ does not », Nature, vol. 294, , p. 188-190 (lire en ligne) DOI 10.1038/294188a0
- (en) F. Meier, B. Suter, H. Grosjean, G. Keith et E. Kubli, « Queuosine modification of the wobble base in tRNAHis influences 'in vivo' decoding properties », EMBO Journal, vol. 4, no 3, , p. 823-827 (lire en ligne)
- (en) Jaunius Urbonavičius, Qiang Qian, Jérôme M.B. Durand, Tord G. Hagervall et Glenn R. Björk, « Improvement of reading frame maintenance is a common function for several tRNA modifications », EMBO Journal, vol. 20, no 17, , p. 4863-4873 (lire en ligne) DOI 10.1093/emboj/20.17.4863
Cet article est issu de wikipedia. Text licence: CC BY-SA 4.0, Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.