Acide minodronique
L'acide minodronique est un bisphosphonate de « troisième génération ». Il a été autorisé au Japon dans le traitement de l'ostéoporose[2]. Son mécanisme d'action implique l'inhibition de la farnésyl pyrophosphate synthase[3].
| Acide minodronique | |
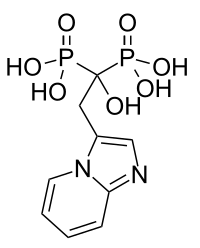
| |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | acide (1-hydroxy-2-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl-1-phosphonoéthyl)phosphonique |
| No CAS | (hydrate) |
| PubChem | 130956 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C9H12N2O7P2 [Isomères] |
| Masse molaire[1] | 322,148 3 ± 0,010 5 g/mol C 33,55 %, H 3,75 %, N 8,7 %, O 34,77 %, P 19,23 %, |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) Shridhar Hegde and Michelle Schmidt, « To Market, To Market - 2009. 16. Minodronic acid », Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry, vol. 45, , p. 509–510
- (en) L.A. Sorbera, J. Castañer et P.A. Leeson, « Minodronic Acid », Drugs of the Future, vol. 27, no 10, , p. 935–941 (DOI 10.1358/dof.2002.027.10.701186)
Cet article est issu de wikipedia. Text licence: CC BY-SA 4.0, Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.