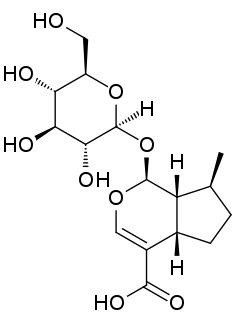
Acide 7-désoxyloganique
L'acide 7-désoxyloganique est un hétéroside d'iridoïde, de formule C16H24O9.
| Acide 7-désoxyloganique | |
| |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | acide (1S,4aS,7S,7aR)-7-méthyl-1-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxyméthyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-1,4a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydrocyclopenta[c]pyran-4-carboxylique |
| No CAS | |
| PubChem | 443322 |
| ChEBI | 2260 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C16H24O9 |
| Masse molaire[1] | 360,356 4 ± 0,017 2 g/mol C 53,33 %, H 6,71 %, O 39,96 %, |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
C'est un métabolite végétal notamment présent chez Crotalaria emarginella et Uncaria tomentosa. Il est synthétisé par l'enzyme acide 7-désoxyloganétique glucosyltransférase (7-DLGT) à partir de l'acide 7-désoxyloganétique[2] - [3]. C'est un substrat de l'enzyme acide 7-désoxyloganique hydroxylase (7-DLH) qui produit l'acide loganique.
Références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- Miettinen, Dong, Navrot, Schneider, Burlat, et al. (2014) The seco-iridoid pathway from Catharanthus roseus. Nat Commun. 5
- Salim, Yu, Altarejos and De Luca (2013) Virus-induced gene silencing identifies Catharanthus roseus 7-deoxyloganic acid-7-hydroxylase, a step in iridoid and monoterpene indole alkaloid biosynthesis. The Plant Journal. 76(5). 754-765
Cet article est issu de wikipedia. Text licence: CC BY-SA 4.0, Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.