Triphosphane
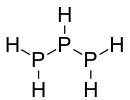
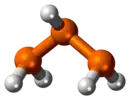
Le triphosphane, ou la triphosphine, est un composé chimique de formule P3H5. C'est l'analogue phosphoré du triazane N3H5. Il peut être obtenu à partir de diphosphane P2H4 mais est très instable à température ambiante[2] :
| Triphosphane | |
  |
|
| Structure du triphosphane | |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Synonymes |
triphosphine |
| No CAS | |
| PubChem | 139510 |
| ChEBI | 35893 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | P3H5 |
| Masse molaire[1] | 97,960 99 ± 0,000 36 g/mol H 5,14 %, P 94,86 %, |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
Les échantillons de triphosphane sont contaminés par du diphosphane P2H4 et du tétraphosphane, P4H6 aussi bien linéaires que ramifiés[3].
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) Norman N. Greenwood et Alan Earnshaw, Chemistry of the Elements, 2e éd., Butterworth-Heinemann, 1997. (ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8)
- (en) Marianne Baudler et Klaus Glinka, « Contributions to the chemistry of phosphorus. 218. Monocyclic and polycyclic phosphines », Chemical Reviews, vol. 93, no 4, , p. 1623-1667 (DOI 10.1021/cr00020a010, lire en ligne)
Cet article est issu de wikipedia. Text licence: CC BY-SA 4.0, Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.