Tectorigénine
La tectorigénine est une isoflavone O-méthylée, un type de flavonoïde. Elle peut notamment être isolée de l'iris domestica (Belamcanda chinensis)[2] ou de Pueraria thunbergiana[3].
| Tectorigénine | |
| |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
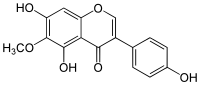
| Nom UICPA | 5,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphényl)-6-méthoxychromén-4-one |
| No CAS | |
| No ECHA | 100.208.621 |
| PubChem | 5281811 |
| SMILES | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C16H12O6 [Isomères] |
| Masse molaire[1] | 300,262 9 ± 0,015 4 g/mol C 64 %, H 4,03 %, O 31,97 %, |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
Hétérosides
La tectoridine est le 7-glucoside de la tectorigénine.
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- Tectorigenin and other phytochemicals extracted from leopard lily Belamcanda chinensis affect new and established targets for therapies in prostate cancer. Paul Thelen, Jens-Gerd Scharf, Peter Burfeind, Bernhard Hemmerlein, Wolfgang Wuttke, Barbara Spengler, Volker Christoffel, Rolf-Hermann Ringert and Dana Seidlová-Wuttke, 2005
- Tectorigenin, an Isoflavone of Pueraria thunbergiana BENTH., Induces Differentiation and Apoptosis in Human Promyelocytic Leukemia HL-60 Cells. Lee Kyung-Tae, Sohn Il-Cheol, Kim Young-Kwan, Choi Jung-Hye, Choi Jong-Won, Park Hee-Juhn, Itoh Yoshie and Miyamoto Ken-ichi, 2001.
Cet article est issu de wikipedia. Text licence: CC BY-SA 4.0, Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.