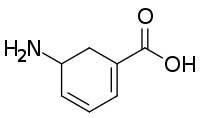
Gabaculine
La gabaculine est une neurotoxine naturelle isolée la première dans la bactérie Streptomyces toyacaensis[2], qui agit comme un puissant et irréversible inhibiteur de la 4-aminobutyrate aminotransférase (GABA transaminase)[3] - [4] ainsi que comme inhibiteur de la recapture du GABA[5] - [6].
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) Kobayashi K, Miyazawa S, Endo A, « Isolation and inhibitory activity of gabaculine, a new potent inhibitor of gamma-aminobutyrate aminotransferase produced by a Streptomyces », FEBS Letters, vol. 76, no 2, , p. 207–10 (PMID 862902, DOI 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80153-1, lire en ligne)
- (en) Rando RR, « Mechanism of the irreversible inhibition of gamma-aminobutyric acid-alpha-ketoglutaric acid transaminase by the neurotoxin gabaculine », Biochemistry, vol. 16, no 21, , p. 4604–10 (PMID 410442, DOI 10.1021/bi00640a012)
- (en) Irifune M, Katayama S, Takarada T, et al., « MK-801 enhances gabaculine-induced loss of the righting reflex in mice, but not immobility », Can J Anaesth, vol. 54, no 12, , p. 998–1005 (PMID 18056209, DOI 10.1007/BF03016634)
- Allan RD, Johnston GAR, Twitchin B. Effects of Gabaculine on uptake, binding and metabolism of GABA. Neuroscience Letters. 1977;4:51-54.
- (en) Høg S, Greenwood JR, Madsen KB, Larsson OM, Frølund B, Schousboe A, Krogsgaard-Larsen P, Clausen RP, « Structure-activity relationships of selective GABA uptake inhibitors », Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, vol. 6, no 17, , p. 1861–82 (PMID 17017962, DOI 10.2174/156802606778249801, lire en ligne)
Cet article est issu de wikipedia. Text licence: CC BY-SA 4.0, Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.