Résolvine
Les résolvines sont des molécules dérivant des acides gras omega 3 : l'acide éicosapentaénoïque (EPA) et l'acide docosahexaénoïque (DHA). Ils sont produits par la voie de la COX-2. Expérimentalement, les résolvines réduisent l'inflammation en "inhibant" la production des molécules inflammatoires et la migration des cellules inflammatoires au site lésionnel. Elles ont montré une efficacité dans le cas de l'insuffisance rénale[1].
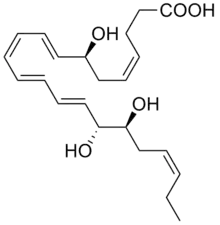
Resolvine D2 (RvD2)
D'autres actions biologiques ont été mises en évidence comme une réduction de la douleur inflammatoire[2]. Elles pourraient également être utile contre la maladie de Parkinson[3], la maladie d'Alzheimer[3], la parodontie[4], contre le cancer[5] - [6], contre le sepsis[7] - [8] - [9] - [10] - [11] - [12].
Liens externes
- (en) Resolvins - A Family of Bioactive Products of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Transformation Circuits Initiated by Aspirin Treatment that Counter Proinflammation Signals, JEM vol. 196no. 81025-1037, The Rockefeller University Press, 21 octobre 2002.
- Xu ZZ, Zhang L, Liu T, Resolvins RvE1 and RvD1 attenuate inflammatory pain via central and peripheral actions, Nat. Med., 2010.
- (en) Santosh Anand, Mohammad Azam Ansari, Sambamurthy Kumaraswamy Sukrutha et Mohammad N. Alomary, « Resolvins Lipid Mediators: Potential Therapeutic Targets in Alzheimer and Parkinson Disease », Neuroscience, vol. 507, , p. 139–148 (DOI 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.11.001, lire en ligne, consulté le )
- (en) Marcela M. Osorio Parra, Satheesh Elangovan et Chun‐Teh Lee, « Specialized pro‐resolving lipid mediators in experimental periodontitis: A systematic review », Oral Diseases, vol. 25, no 5, , p. 1265–1276 (ISSN 1354-523X et 1601-0825, DOI 10.1111/odi.12979, lire en ligne, consulté le )
- (en) Dipak Panigrahy, Allison Gartung, Jun Yang et Haixia Yang, « Preoperative stimulation of resolution and inflammation blockade eradicates micrometastases », Journal of Clinical Investigation, vol. 129, no 7, , p. 2964–2979 (ISSN 0021-9738 et 1558-8238, PMID 31205032, PMCID PMC6597207, DOI 10.1172/JCI127282, lire en ligne, consulté le )
- Kai Shan, Ninghan Feng, Jing Cui et Shunhe Wang, « Resolvin D1 and D2 inhibit tumour growth and inflammation via modulating macrophage polarization », Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, vol. 24, no 14, , p. 8045–8056 (ISSN 1582-4934, PMID 32469149, PMCID 7348143, DOI 10.1111/jcmm.15436, lire en ligne, consulté le )
- (en) F. Chen, X. H. Fan, Y. P. Wu et J. L. Zhu, « Resolvin D1 improves survival in experimental sepsis through reducing bacterial load and preventing excessive activation of inflammatory response », European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases, vol. 33, no 3, , p. 457–464 (ISSN 0934-9723 et 1435-4373, DOI 10.1007/s10096-013-1978-6, lire en ligne, consulté le )
- Matthew Spite, Lucy V. Norling, Lisa Summers et Rong Yang, « Resolvin D2 is a potent regulator of leukocytes and controls microbial sepsis », Nature, vol. 461, no 7268, , p. 1287–1291 (ISSN 0028-0836, PMID 19865173, PMCID 2779525, DOI 10.1038/nature08541, lire en ligne, consulté le )
- (en) Matthias Hecker, Natascha Sommer, Sebastian Foch et Andreas Hecker, « Resolvin E1 and its precursor 18R-HEPE restore mitochondrial function in inflammation », Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids, vol. 1863, no 9, , p. 1016–1028 (ISSN 1388-1981, DOI 10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.06.011, lire en ligne, consulté le )
- (en) Menglong Wang, Menglin Liu, Jishou Zhang et Jianfang Liu, « Resolvin D1 protects against sepsis‐induced cardiac injury in mice », BioFactors, vol. 46, no 5, , p. 766–776 (ISSN 0951-6433 et 1872-8081, DOI 10.1002/biof.1668, lire en ligne, consulté le )
- Bing Xu, Mi Li, Tingting Cheng et Jun Xia, « Resolvin D1 protects against sepsis-associated encephalopathy in mice by inhibiting neuro-inflammation induced by microglia », American Journal of Translational Research, vol. 14, no 9, , p. 6737–6750 (ISSN 1943-8141, PMID 36247289, PMCID 9556482, lire en ligne, consulté le )
- Bakr Jundi, Do-Hyun Lee, Hyungkook Jeon et Melody G. Duvall, « Inflammation resolution circuits are uncoupled in acute sepsis and correlate with clinical severity », JCI insight, vol. 6, no 15, , e148866 (ISSN 2379-3708, PMID 34166226, PMCID 8410067, DOI 10.1172/jci.insight.148866, lire en ligne, consulté le )
Cet article est issu de wikipedia. Text licence: CC BY-SA 4.0, Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.