Jicarillas
Les Jicarillas sont un groupe d'Apaches vivant dans le Sud-Ouest des États-Unis.
Jicarillas

Jeune garçon Jicarilla en 2009.
| Population totale | 3300[1] |
|---|
| Régions d’origine |
|
|---|---|
| Langues | anglais, jicarilla |
| Religions | Christianisme, religion traditionnelle tribale, Native American Church |
| Ethnies liées | Chiricahuas, Apaches des Plaines, Lipans, Mescaleros, Navajos, Tonto, Apaches de l'Ouest |
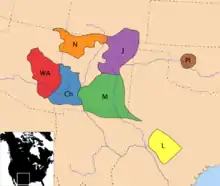
Répartition des tribus apaches au XVIIIe siècle : Ch – Chiricahuas, WA – Apaches de l'Ouest, N – Navajos, M – Mescaleros, J – Jicarillas, L – Lipans, Pl – Apaches des Plaines.
Le Jicarilla Apache ( espagnol: [xikaˈɾiʝa] , langue Jicarilla : Jicarilla Dindéi ), l'un des nombreuses groupes autonomes de l' Apache oriental , fait référence aux membres de la nation Jicarilla Apache vivant actuellement au Nouveau-Mexique et parlant une langue du sud de l'Athabaskan . Le terme jicarilla vient de l'espagnol mexicain et signifierait "petit panier"[2]
Pour les groupes Apache voisins, tels que les Mescaleros et les Lipan, ils étaient connus sous le nom de Kinya-Inde ("Les gens qui vivent dans des maisons fixes").
Personnes Notables
- James Garfield Velarde, chef du XIXe siècle, représenté sur la couverture du single She_Sells_Sanctuary du groupe The_Cult
- Francisco_Chacon, chef du XIXe siècle, chef du soulèvement de Jicarilla en 1854
- Flechas_Rayadas, chef du XIXe siècle, impliqué dans le soulèvement de Jicarilla en 1854
- Lobo_Blanco, chef du XIXe siècle tué en 1854
- Viola_Cordova (née en 1937), philosophe
- Tammie_Allen (née en 1964), potière
Notes et références
Références
- "Historic Jicarilla Apache Land." Jicarilla Apache Nation. (consulté le 9 juin 2017)
- (en) « Jicarilla Encyclopedia Britianica »
Voir aussi
Articles connexes
- Dialogue de feu, film de 1971 financé par les Jicarillas.
- Langue jicarilla
- Liste des réserves indiennes aux États-Unis
Bibliographie
- Brooks, Clinton E.; Reeve, Frank D.; Bennett, James A. (1996). Forts and Forays: James A. Bennett, A Dragoon in New Mexico, 1850—1856. University of New Mexico Press. (ISBN 0-8263-1690-5).
- Cassells, E. Steve. (1997). The Archeology of Colorado, Revised Edition. Boulder, Colorado: Johnson Books. (ISBN 1-55566-193-9).
- Carlisle, Jeffrey D. (May 2001). "Spanish Relations with the Apache Nations east of the Rio Grande". University of North Texas.
- Carter, Harvey Lewis. (1990) "Dear Old Kit": The Historical Christopher Carson, University of Oklahoma Press. (ISBN 0-8061-2253-6).
- Davidson, Homer K. (1974). Black Jack Davidson, A Cavalry Commander on the Western Frontier: The Life of General John W. Davidson. A. H. Clark Co. Page 72. (ISBN 0-87062-109-2).
- Eiselt, B. Sunday. (2009) The Jicarilla Apaches and the Archaeology of the Taos Region. Between the Mountains – Beyond the Mountains. Papers of the Archaeological Society of New Mexico Vol. 35, Albuquerque.
- Gibbon, Guy E.; Ames, Kenneth M. (1998) Archaeology of Prehistoric Native America: An Encyclopedia. (ISBN 0-8153-0725-X).
- Goddard, Pliny E. (1911). Jicarilla Apache texts. Anthropological papers of the American Museum of Natural History (Vol. 8). New York: The American Museum of Natural History.
- Gorenfeld, Will. (Feb, 2008). "The Battle of Cieneguilla." Wild West magazine.
- Greenwald, Emily. (2002). Reconfiguring the reservation: The Nez Perces, Jicarilla Apache and the Dawes Act. University of New Mexico Press. (ISBN 0-8263-2408-8).
- Griffin-Pierce, Trudy. (2000). Native Peoples of the Southwest. University of New Mexico Press. (ISBN 0-8263-1908-4).
- Hook, Jason; Pegler, Martin. (2001). To Love and Die in the West: the American Indian Wars, 1860-90. Chicago: Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers. (ISBN 1-57958-370-9).
- Kessel, William B.; Wooster, Robert. (ed.) (2005). Encyclopedia of Native American Wars and Warfare. New York: Facts on File. (ISBN 0-8160-3337-4).
- King, Lesley S. (2011). Frommer's New Mexico Hoboken, NJ: Wiley Publishing. (ISBN 978-0-470-87617-6).
- Martin, Craig. (ed.) (2002). Fly Fishing in Northern New Mexico. University of New Mexico Press. (ISBN 978-0-8263-2761-1).
- Oliva, Leo E. (1993).Fort Union and the Frontier Army in the Southwest: Fort Union, New Mexico Military Operations Before the Civil War. National Park Service Online Books.
- Pritzker, Barry M. (2000). A Native American Encyclopedia: History, Culture, and Peoples. Oxford: Oxford University Press. (ISBN 978-0-19-513877-1).
- Rajtar, Steve. (1999) Indian War Sites: A Guidebook to Battlefields, Monuments, and Memorials. Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland & Company, Inc.
- Velarde Tiller, Veronica E. (2011) Culture and Customs of the Apache Indians. Santa Barbara, CA: Greenwood of ABC-CLIO. (ISBN 978-0-313-36452-5).
- Warren, Nancy Hunter; Velarde Tiller, Veronica E. (2006). The Jicarilla Apache: A Portrait. University of New Mexico Press. (ISBN 0-8263-3776-7).
Lien externe
Cet article est issu de wikipedia. Text licence: CC BY-SA 4.0, Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.
.jpg.webp)
