HyperNEAT
Le NEAT basé sur l'hypercube, ou HyperNEAT[1] est un codage génératif pour évoluer des réseaux de neurones artificiels (ANN) avec les principes de l'algorithme NeuroEvolution of Augmented Topologies (NEAT) développé par Kenneth Stanley[2]. Il s'agit d'une nouvelle technique pour faire évoluer des réseaux de neurones à grande échelle en utilisant les régularités géométriques du domaine de la tâche.
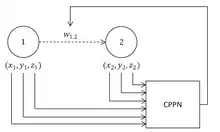
L'encodage génétique est indirect. L'algorithme utilise des réseaux de production de motifs de composition[3] ( CPPN ), qui sont utilisés pour générer les images pour Picbreeder.org et les formes pour EndlessForms.com. HyperNEAT a récemment été étendu pour faire évoluer également des réseaux de neurones artificiel plastique[4] et pour faire évoluer l'emplacement de chaque neurone du réseau[5].
Quelques exemples d'utilisation
- Apprentissage multi-agents[6]
- Évaluation du jeu de dames[7]
- Contrôler les robots à pattes[8] - [9] - [10] - [11] - [12] - [13] vidéo
- Comparer Génératif vs. Encodages directs[14] - [15] - [16]
- Enquêter sur l'évolution des réseaux de neurones modulaires[17] - [18] - [19]
- Objets évolutifs pouvant être imprimés en 3D[20]
- Évolution de la géométrie neurale et de la plasticité d'un ANN[21]
Références
- Stanley, D'Ambrosio et Gauci, « A Hypercube-Based Encoding for Evolving Large-Scale Neural Networks », Artificial Life, vol. 15, no 2, , p. 185–212 (ISSN 1064-5462, PMID 19199382, DOI 10.1162/artl.2009.15.2.15202, S2CID 26390526, lire en ligne)
- Stanley et Miikkulainen, « Evolving Neural Networks through Augmenting Topologies », Evolutionary Computation, vol. 10, no 2, , p. 99–127 (ISSN 1063-6560, PMID 12180173, DOI 10.1162/106365602320169811, S2CID 498161, CiteSeerx 10.1.1.638.3910)
- (en) Stanley, « Compositional pattern producing networks: A novel abstraction of development », Genetic Programming and Evolvable Machines, vol. 8, no 2, , p. 131–162 (ISSN 1389-2576, DOI 10.1007/s10710-007-9028-8, S2CID 2535195, CiteSeerx 10.1.1.643.8179)
- (en) Sebastian Risi et Kenneth O. Stanley, From Animals to Animats 11, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, coll. « Lecture Notes in Computer Science », , 533–543 p. (ISBN 9783642151927, DOI 10.1007/978-3-642-15193-4_50, CiteSeerx 10.1.1.365.5589)
- Risi et Stanley, « An Enhanced Hypercube-Based Encoding for Evolving the Placement, Density, and Connectivity of Neurons », Artificial Life, vol. 18, no 4, , p. 331–363 (ISSN 1064-5462, PMID 22938563, DOI 10.1162/ARTL_a_00071, S2CID 3256786, lire en ligne)
- David B. D'Ambrosio et Kenneth O. Stanley, Generative Encoding for Multiagent Learning, New York, NY, USA, ACM, coll. « GECCO '08 », , 819–826 p. (ISBN 9781605581309, DOI 10.1145/1389095.1389256, S2CID 11507017)
- J. Gauci and K. O. Stanley, “A case study on the critical role of geometric regularity in machine learning,” in AAAI (D. Fox and C. P. Gomes, eds.), pp. 628–633, AAAI Press, 2008.
- Sebastian Risi et Kenneth O. Stanley, Confronting the Challenge of Learning a Flexible Neural Controller for a Diversity of Morphologies, New York, NY, USA, ACM, coll. « GECCO '13 », , 255–262 p. (ISBN 9781450319638, DOI 10.1145/2463372.2463397, S2CID 10308013, CiteSeerx 10.1.1.465.5068)
- J. Clune, B. E. Beckmann, C. Ofria et R. T. Pennock, Evolving coordinated quadruped gaits with the HyperNEAT generative encoding, , 2764–2771 p. (ISBN 978-1-4244-2958-5, DOI 10.1109/CEC.2009.4983289, S2CID 17566887, CiteSeerx 10.1.1.409.3868)
- Jeff Clune, Charles Ofria et Robert T. Pennock, The Sensitivity of HyperNEAT to Different Geometric Representations of a Problem, New York, NY, USA, ACM, coll. « GECCO '09 », , 675–682 p. (ISBN 9781605583259, DOI 10.1145/1569901.1569995, S2CID 16054567)
- Yosinski J, Clune J, Hidalgo D, Nguyen S, Cristobal Zagal J, Lipson H (2011) Evolving Robot Gaits in Hardware: the HyperNEAT Generative Encoding Vs. Parameter Optimization. Proceedings of the European Conference on Artificial Life. (pdf)
- Lee S, Yosinski J, Glette K, Lipson H, Clune J (2013) Evolving gaits for physical robots with the HyperNEAT generative encoding: the benefits of simulation. Applications of Evolutionary Computing. Springer. pdf
- (en) Suchan Lee, Jason Yosinski, Kyrre Glette, Hod Lipson et Clune, Applications of Evolutionary Computation, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, coll. « Lecture Notes in Computer Science », , 540–549 p. (ISBN 9783642371912, DOI 10.1007/978-3-642-37192-9_54, CiteSeerx 10.1.1.364.8979)
- Clune, Stanley, Pennock et Ofria, « On the Performance of Indirect Encoding Across the Continuum of Regularity », IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 15, no 3, , p. 346–367 (ISSN 1089-778X, DOI 10.1109/TEVC.2010.2104157, S2CID 3008628, CiteSeerx 10.1.1.375.6731)
- (en) Jeff Clune, Charles Ofria et Robert T. Pennock, Parallel Problem Solving from Nature – PPSN X, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, coll. « Lecture Notes in Computer Science », , 358–367 p. (ISBN 9783540876991, DOI 10.1007/978-3-540-87700-4_36)
- (en) Jeff Clune, Benjamin E. Beckmann, Robert T. Pennock et Charles Ofria, Advances in Artificial Life. Darwin Meets von Neumann, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, coll. « Lecture Notes in Computer Science », , 134–141 p. (ISBN 9783642213137, DOI 10.1007/978-3-642-21314-4_17, CiteSeerx 10.1.1.409.741)
- Jeff Clune, Benjamin E. Beckmann, Philip K. McKinley et Charles Ofria, Investigating Whether hyperNEAT Produces Modular Neural Networks, New York, NY, USA, ACM, coll. « GECCO '10 », , 635–642 p. (ISBN 9781450300728, DOI 10.1145/1830483.1830598, S2CID 14826185, CiteSeerx 10.1.1.409.4870)
- Marcin Suchorzewski et Jeff Clune, A Novel Generative Encoding for Evolving Modular, Regular and Scalable Networks, New York, NY, USA, ACM, coll. « GECCO '11 », , 1523–1530 p. (ISBN 9781450305570, DOI 10.1145/2001576.2001781, S2CID 2542736, CiteSeerx 10.1.1.453.5744)
- Phillip Verbancsics et Kenneth O. Stanley, Constraining Connectivity to Encourage Modularity in HyperNEAT, New York, NY, USA, ACM, coll. « GECCO '11 », , 1483–1490 p. (ISBN 9781450305570, DOI 10.1145/2001576.2001776, S2CID 1442181, CiteSeerx 10.1.1.379.1188)
- Clune et Lipson, « Evolving 3D Objects with a Generative Encoding Inspired by Developmental Biology », SIGEVOlution, vol. 5, no 4, , p. 2–12 (ISSN 1931-8499, DOI 10.1145/2078245.2078246, S2CID 9566239)
- S. Risi et K. O. Stanley, A unified approach to evolving plasticity and neural geometry, , 1–8 p. (ISBN 978-1-4673-1490-9, DOI 10.1109/IJCNN.2012.6252826, S2CID 14268194, CiteSeerx 10.1.1.467.8366)